2 Study Area
2.1 Description
Located in southcentral Alaska, the Kenai River is part of the Cook Inlet Basin and is linked to the surrounding communities through sport, commercial, personal use, and susbsistence fishing; as well as tourism, and recreation (Figure 2.1). At least twenty-seven fish species, including six species of anadromous Pacific salmonids flourish in the Kenai River watershed, with sockeye (red) and Chinook (king) salmon as the primary species of interest for harvest and sport fisheries (Schoen et al. 2017; Willette, Edmundson, and DeCino 2004). The Kenai River his historically produced 80% of the sockeye harvested in Cook Inlet (Dorava and Milner 2000).
Surface runoff, groundwater composition, natural minerals, aquatic plants and animals, and human activities can affect water quality in this area. Potential sources of pollution from humans include gasoline powered boat engines, agriculture, mining, street runoff, and perforated septic tanks (Glass, RL 1999; Reeves et al. 2018; EPA 2011).
2.2 Figures/maps
2.2.1 Online Map of Sample Sites
Access ArcGIS Online project map at https://arcg.is/0LXGSf
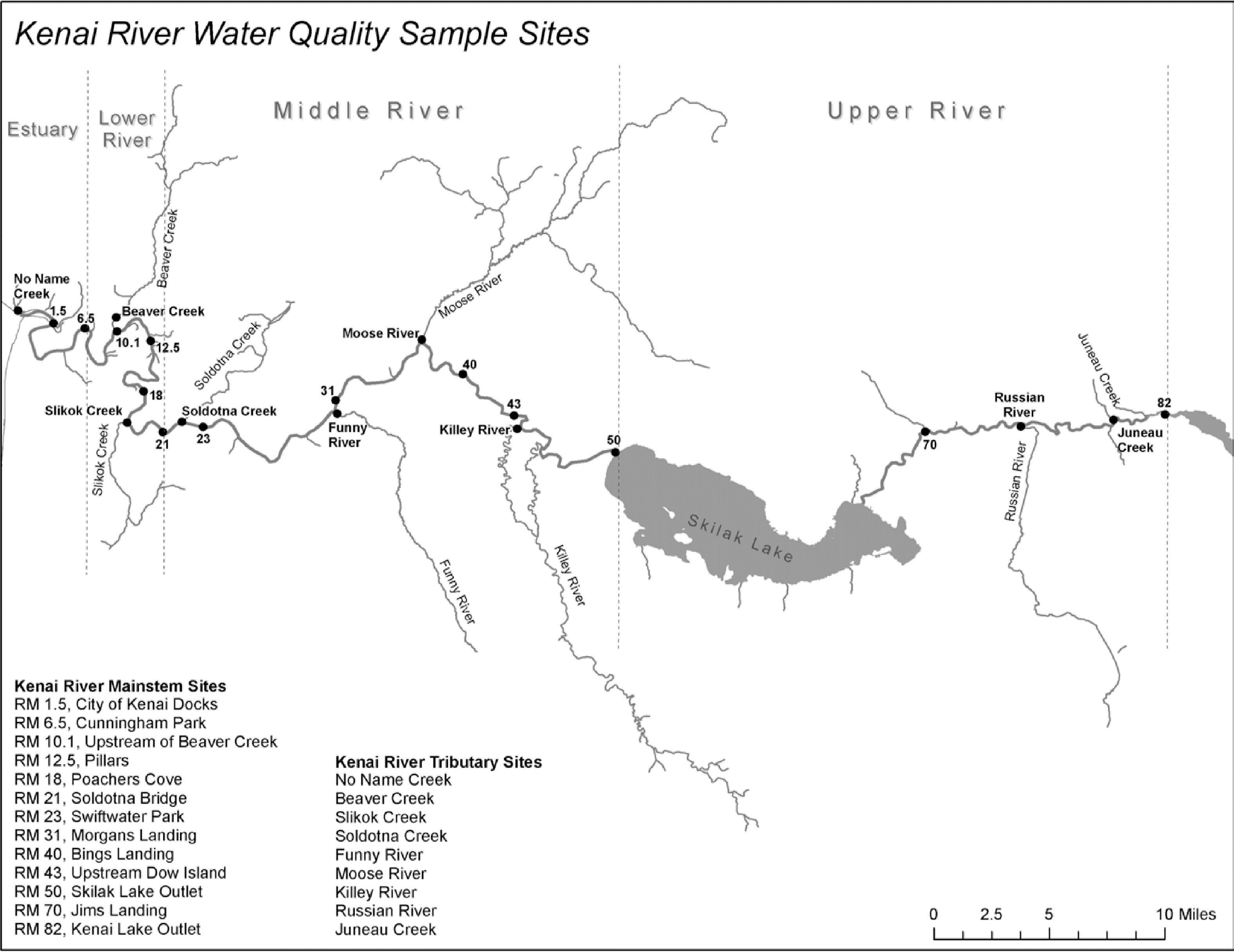
2.3 Sampling sites descriptions/photos
Field sampling sites described in Figure 2.2 are introduced below with a photo a coordinates for each location.
2.3.1 Tributary Sites
2.3.1.1 No Name Creek
No Name Creek is a Kenai River tributary located at 60.550888 N and -151.268417 W. Samples are typically collected approximately 500 feet upstream of the confluence with the Kenai River, just upstream of the footbridge.

2.3.1.2 Beaver Creek
Beaver Creek is a Kenai River tributary. Sample site is located at 60.548029 N and -151.143240 W.
2.3.1.3 Slikok Creek
2.3.1.4 Soldotna Creek
2.3.1.5 Funny River
2.3.1.6 Moose River
2.3.1.7 Killey River
2.3.1.8 Russian River
2.3.1.9 Juneau Creek
2.3.2 Main Stem Sites
This section will include a brief description of each of the main stem field sampling sites, along with coordinates and a photo.
